SurfaceTreat
PLASMA – green technology of surface treatment
Equipment for contrast enhancement on interface of materials and particular different phases of microstructure in optical microscopy
Definition
- Equipment for optimal material structure visualization (enhancement of the dark areas and elimination of light areas and reflections mainly of surface layers or surface treated materials), visualization of material defects using optical microscopy.
- Equipment enables perfect visualization of the contrast of different types of material in one place and their interface, which is not usually possible or only with difficulty with some kind of compromise for glazed or etched samples
- Samples preparation is very quick (ca 5 min) in dependence on the sample material and material used for encapsulation
- Alternative method for the dangerous substances used for metalography

Cast iron with spheroidal graphite after galvanic treatment ZnNi and powder coating – microsection of the defect
Sample encapsulated in thermo set resin DuroFast180°/325 bar/5 min., glazed using colloid silica, photo Leica DM 2500 (left side figure), deposited by FeO – 3 min. / 3 mA (right side figure). Benefit of application after sputtering visual in the area marked with arrows (click for zoom).
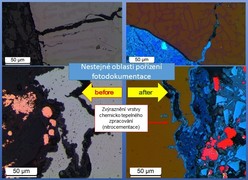
Fe3Al (experimental material developed and tested by Technical University in Liberec, (Mechanical Engineering faculty, Department of materials) – visualization of surface layer after nitrocarburising.
Sample encapsulated in thermo set resin with Cu filler, glazed using colloid silica, photo Leica DM 2500 (left side figure), deposited by FeO – 4 min./2,7 mA (right side figure). Benefit of application after sputtering visual in the area marked with arrows (click for zoom).

AlSi cast after anodizing and coating – visualization of metallic filler coloration in paint
Sample encapsulated in thermo set resin EpoFix, glazed using colloid silica, photo Leica DM 2500 (left side figure), deposited by FeO – 5 min./1,7 mA (right side figure). Benefit of application after sputtering visual in the area marked with arrows (click for zoom).
Application examples with significant benefit in the area of visualisation (photodocumentation)
Metalography (microsections):
- o glass fibers in PCB materials – printed circuit boards
- o inhomogenous materials, composites, resin with fillers
- o microstructure of plastics with fillers
- o lacquer coatings (transparent/colored)
- o partially also microstructures of metals in sintered states (steel, solder, cast iron, etc.) – currently in development

Flaked layer on the stell surface
Sample encapsulated in thermo set resin DuroFast, glazed using colloid silica, photo Leica DM 2500 (left side figure), deposited by FeO – 3 min./3 mA (right side figure). Benefit of application after sputtering visual in the area of the basic material (steel) mainly in different coloration of ferrite and pearlite (click for zoom).

PCB after soldering using Sn solder – visualisation of so called barrel crack
Sample encapsulated in thermo set resin EpoFix, glazed using colloid silica, photo Leica DM 2500 (left side figure), deposited by FeO – 4-5 min./2 mA (right side figure). Benefit of application after sputtering visual in the area marked with arrows (click for zoom).

PCB after soldering using Sn solder – interference contrast of the basic material PCB and Cu layer
Sample encapsulated in thermo set resin Technovit 4001, glazed using colloid silica, photo Leica DM 2500 (left side figure), deposited by FeO – 3 min./3 mA (right side figure). Benefit of application after sputtering visual in the area marked with arrows (click for zoom).

Steel forged piece after surface galvanization using ZnNi and multilayer lacquering – microsection in the impurity between the lacquer layers
Sample encapsulated in thermo set resin DuroFast 180° / 325 bar / 5 min, glazed using colloid silica, photo Leica DM 2500 (left side figure), deposited by FeO – 3 min./3 mA 2x (right side figure). Benefit of application after sputtering visual in the area marked with arrows (click for zoom).
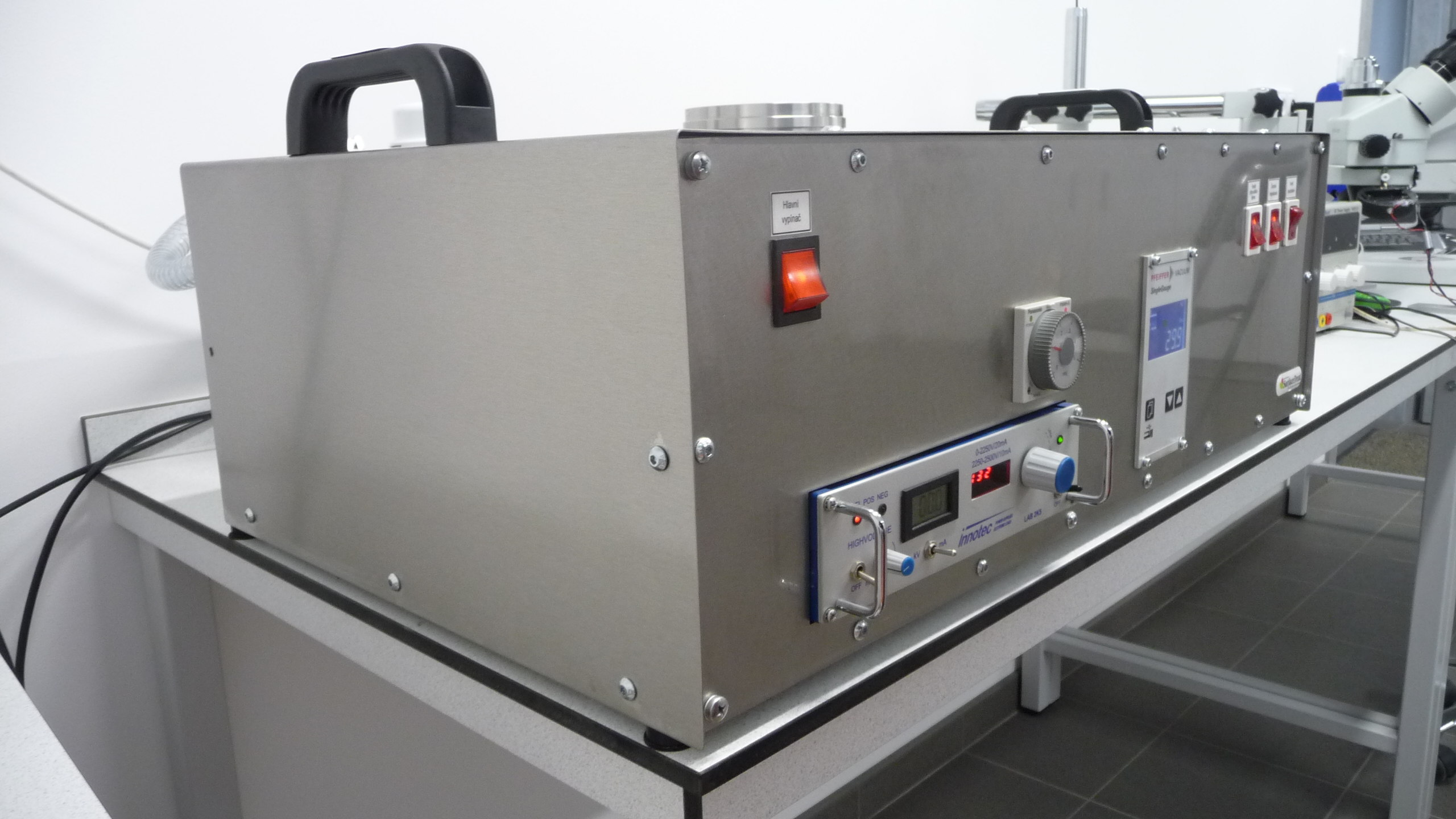

Description of the equipment for contrast enhancement on interface of materials in optical microscopy – Contrast enhancement chamber
- Main switch
- Vacuum chamber
- Venting valve
- Angle valve (Avoid damage of the plastic knob. Handle with care!)
- Dosing valve
- Vacuum gauge – in front, sensor on the back side
- Rotary pump with oil filter in the gas outlet
- High voltage supply
- Timer

Detail of the vacuum chamber
a) Detailed view of the vacuum chamber with sample holder in place
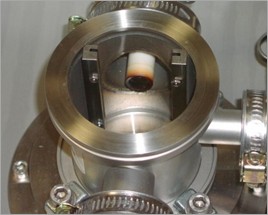
Detail of the vacuum chamber
b) Detailed view of the vacuum chamber; the sample holder is removed and the iron target can be seen
Limitations connected with sample preparation
- „fresh samples“, i.e. immediately after glazing, clearing and drying – capillarity effect of the impurities from resin or pits during evacuation
- it is necessary to choose optimum resin type to eliminate a gap between surface layer and the resin (micro gap between sample surface inside and resin around), because of impurities and moisture capillary effect
- samples made of thin plastic fibers and epoxy resins are very sensitive to plasma radiation, therefore it is necessary to deposit FeO repeatedly under lower supply or using longer treatment time
Proudly created by Meatballs, s.r.o., 2017